Congratulations Stephen Baker
Professor Stephen Baker recently published an article in Communications Medicine titled “Plasma from patients with pulmonary embolism show aggregates that reduce after anticoagulation”. The intriguing background story behind this study can be accessed here.
.

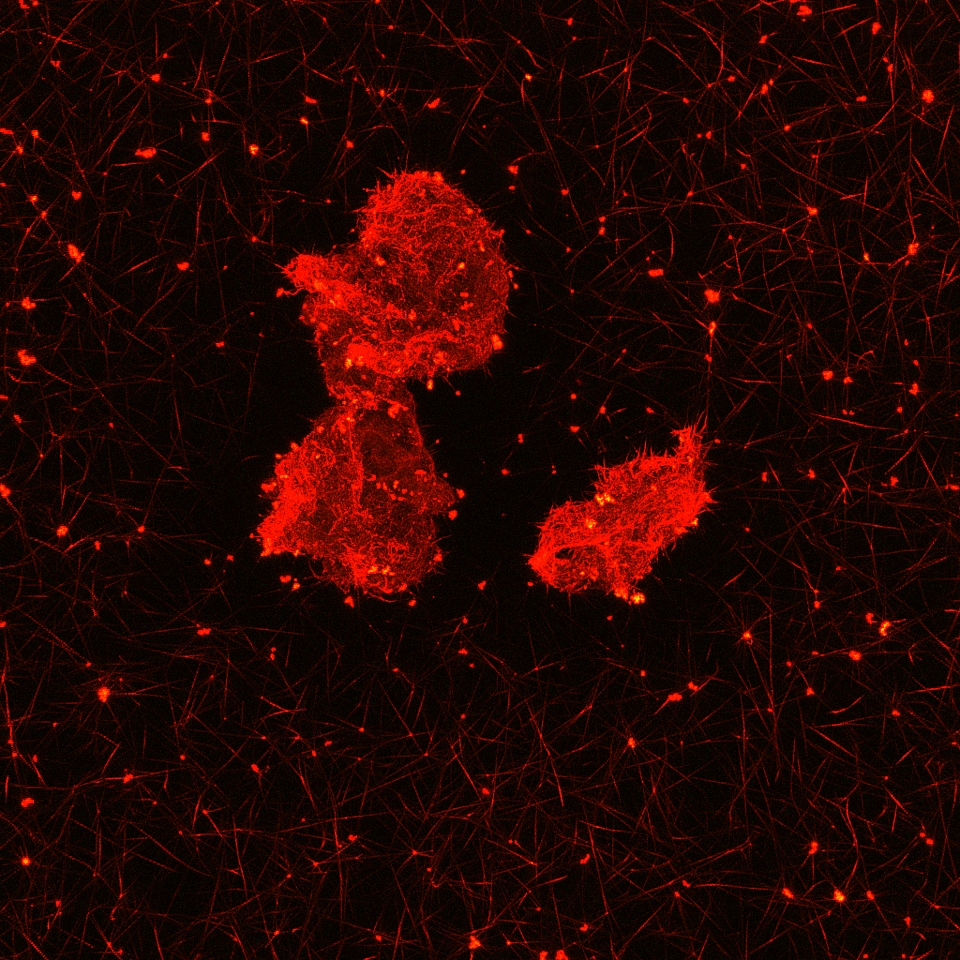
Professor Baker’s study investigates the formation of blood clots in patients with pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism is a life threatening condition which occurs when a blood clot lodges in the artery of a lung, stopping blood flow to that part of the lung. Baker’s study found that small atypical aggregates consisting of fibrin proteins and platelet cells exist in the blood of people with pulmonary embolism, an occurrence which has also been observed in patients with COVID-19. This discovery could help to understand the cause of diseases associated with blood clotting and hopefully to formulate new approaches to treatment.
